跟踪一个.where().order()和#each
完整trace
class ArticlesController < ApplicationController
def index
@articles = binding.trace_tree(html: true, tmp: ['rails', 'where_order.html']) do
Article.where('title <> ?', 1).order(title: :asc)
end
endclass ArticlesController < ApplicationController
def index
@articles = Article.where('title <> ?', 1).order(title: :asc)
binding.trace_tree(timer: true, html: true, tmp: ['rails', 'relation_each.html']) do
@articles.each(&:object_id)
end
end.where().order()
首先,所有查询方法(?)都会委托到all
module ActiveRecord
module Querying
delegate :find, :take, :take!, :first, :first!, :last, :last!, :exists?, :any?, :many?, :none?, :one?, to: :all
delegate :second, :second!, :third, :third!, :fourth, :fourth!, :fifth, :fifth!, :forty_two, :forty_two!, :third_to_last, :third_to_last!, :second_to_last, :second_to_last!, to: :all
delegate :first_or_create, :first_or_create!, :first_or_initialize, to: :all
delegate :find_or_create_by, :find_or_create_by!, :find_or_initialize_by, to: :all
delegate :find_by, :find_by!, to: :all
delegate :destroy, :destroy_all, :delete, :delete_all, :update, :update_all, to: :all
delegate :find_each, :find_in_batches, :in_batches, to: :all
delegate :select, :group, :order, :except, :reorder, :limit, :offset, :joins, :left_joins, :left_outer_joins, :or,
:where, :rewhere, :preload, :eager_load, :includes, :from, :lock, :readonly,
:having, :create_with, :uniq, :distinct, :references, :none, :unscope, to: :all
delegate :count, :average, :minimum, :maximum, :sum, :calculate, to: :all
delegate :pluck, :ids, to: :all而all实际上是返回一个ActiveRecord::Relation
module ActiveRecord
module Scoping
module Named
extend ActiveSupport::Concern
module ClassMethods
def all
if current_scope
current_scope.clone
else
default_scoped
end
end
def default_scoped # :nodoc:
scope = build_default_scope
if scope
relation.spawn.merge!(scope)
else
relation
end
endActiveRecord::Relation是可以链式调用的,利用的是spawn来生成一个新的ActiveRecord::Relation
def where(opts = :chain, *rest)
if :chain == opts
WhereChain.new(spawn)
elsif opts.blank?
self
else
spawn.where!(opts, *rest)
end
end
基本上所有查询方法(?)都会用spawn来新建一个Relation,然后在其之上配置查询条件
$ gems git:(master) grep spawn activerecord-5.0.2/lib/active_record/relation/query_methods.rb
spawn.includes!(*args)
spawn.eager_load!(*args)
spawn.preload!(*args)
spawn.references!(*table_names)
spawn._select!(*fields)
spawn.group!(*args)
spawn.order!(*args)
spawn.reorder!(*args)
spawn.unscope!(*args)
spawn.joins!(*args)
spawn.left_outer_joins!(*args)
WhereChain.new(spawn)
spawn.where!(opts, *rest)
spawn.or!(other)
opts.blank? ? self : spawn.having!(opts, *rest)
spawn.limit!(value)
spawn.offset!(value)
spawn.lock!(locks)
spawn.readonly!(value)
spawn.create_with!(value)
spawn.from!(value, subquery_name)
spawn.distinct!(value)
spawn.extending!(*modules, &block)
spawn.reverse_order!spawn就是简单地clone
module ActiveRecord
module SpawnMethods
# This is overridden by Associations::CollectionProxy
def spawn #:nodoc:
clone
end而为了避免Relation重用时修改到查询条件,需要对保存查询条件的@values进行深复制
module ActiveRecord
class Relation
def initialize_copy(other)
@values = Hash[@values]
reset
end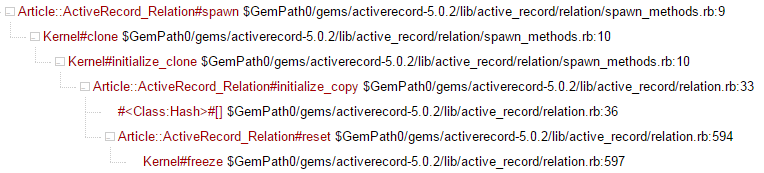
复制之后就是塞条件了
# activerecord-5.0.2/lib/active_record/relation/query_methods.rb
def where!(opts, *rest) # :nodoc:
opts = sanitize_forbidden_attributes(opts)
references!(PredicateBuilder.references(opts)) if Hash === opts
self.where_clause += where_clause_factory.build(opts, rest)
self
endwhere_clause定义如下
# activerecord-5.0.2/lib/active_record/relation/query_methods.rb
Relation::CLAUSE_METHODS.each do |name|
class_eval <<-CODE, __FILE__, __LINE__ + 1
def #{name}_clause # def where_clause
@values[:#{name}] || new_#{name}_clause # @values[:where] || new_where_clause
end # end
#
def #{name}_clause=(value) # def where_clause=(value)
assert_mutability! # assert_mutability!
@values[:#{name}] = value # @values[:where] = value
end # end
CODE
endActiveRecord::Relation底下还有各种constant
irb(main):005:0> puts ActiveRecord::Relation.constree
ActiveRecord::Relation (Class)
├─MULTI_VALUE_METHODS (Array)
├─SINGLE_VALUE_METHODS (Array)
├─CLAUSE_METHODS (Array)
├─INVALID_METHODS_FOR_DELETE_ALL (Array)
├─VALUE_METHODS (Array)
├─HashMerger (Class)
├─Merger (Class)
│ ├─NORMAL_VALUES (Array)
│ └─CLAUSE_METHOD_NAMES (Array)
├─FromClause (Class)
├─QueryAttribute (Class)
│ └─UserProvidedDefault (Class)
│ └─UserProvidedDefault → ActiveRecord::Relation::QueryAttribute::UserProvidedDefault
├─WhereClause (Class)
│ └─ARRAY_WITH_EMPTY_STRING (Array)
├─WhereClauseFactory (Class)
├─ONE_AS_ONE (String)
├─WhereChain (Class)
├─FROZEN_EMPTY_ARRAY (Array)
├─FROZEN_EMPTY_HASH (Hash)
├─VALID_UNSCOPING_VALUES (Set)
├─VALID_DIRECTIONS (Array)
├─BatchEnumerator (Class)
├─ORDER_OR_LIMIT_IGNORED_MESSAGE (String)
├─DelegateCache (Module)
├─ClassSpecificRelation (Module)
│ └─ClassMethods (Module)
└─ClassMethods (Module)
=> nil不过现在关注的主要是XX_METHODS
module ActiveRecord
class Relation
MULTI_VALUE_METHODS = [:includes, :eager_load, :preload, :select, :group,
:order, :joins, :left_joins, :left_outer_joins, :references,
:extending, :unscope]
SINGLE_VALUE_METHODS = [:limit, :offset, :lock, :readonly, :reordering,
:reverse_order, :distinct, :create_with]
CLAUSE_METHODS = [:where, :having, :from]order同理,spawn后,塞查询条件
def order(*args)
check_if_method_has_arguments!(:order, args)
spawn.order!(*args)
end
def order!(*args) # :nodoc:
preprocess_order_args(args)
self.order_values += args
self
endorder_values定义如下
Relation::MULTI_VALUE_METHODS.each do |name|
class_eval <<-CODE, __FILE__, __LINE__ + 1
def #{name}_values
@values[:#{name}] || FROZEN_EMPTY_ARRAY
end
def #{name}_values=(values)
assert_mutability!
@values[:#{name}] = values
end
CODE
end#each
所有的类Enumerable方法(?)都会委托到records方法返回的@records上
module ActiveRecord
module Delegation
delegate :to_xml, :encode_with, :length, :collect, :map, :each, :all?, :include?, :to_ary, :join,
:[], :&, :|, :+, :-, :sample, :reverse, :compact, :in_groups, :in_groups_of,
:to_sentence, :to_formatted_s,
:shuffle, :split, :index, to: :recordsrecords所做的就是exec_queries,缓存@records,并标记@load为true,以使下次不用再exec_queries
module ActiveRecord
class Relation
attr_reader :table, :klass, :loaded, :predicate_builder
alias :model :klass
alias :loaded? :loaded
def records
load
@records
end
def load(&block)
exec_queries(&block) unless loaded?
self
end
private
def exec_queries(&block)
@records = eager_loading? ? find_with_associations.freeze : @klass.find_by_sql(arel, bound_attributes, &block).freeze
preload = preload_values
preload += includes_values unless eager_loading?
preloader = build_preloader
preload.each do |associations|
preloader.preload @records, associations
end
@records.each(&:readonly!) if readonly_value
@loaded = true
@records
endfind_by_sql所使用的arel对象的生成如下
# activerecord-5.0.2/lib/active_record/relation/query_methods.rb
def arel
@arel ||= build_arel
end
def build_arel
arel = Arel::SelectManager.new(table)
build_joins(arel, joins_values.flatten) unless joins_values.empty?
build_left_outer_joins(arel, left_outer_joins_values.flatten) unless left_outer_joins_values.empty?
arel.where(where_clause.ast) unless where_clause.empty?
arel.having(having_clause.ast) unless having_clause.empty?
if limit_value
if string_containing_comma?(limit_value)
arel.take(connection.sanitize_limit(limit_value))
else
arel.take(Arel::Nodes::BindParam.new)
end
end
arel.skip(Arel::Nodes::BindParam.new) if offset_value
arel.group(*arel_columns(group_values.uniq.reject(&:blank?))) unless group_values.empty?
build_order(arel)
build_select(arel)
arel.distinct(distinct_value)
arel.from(build_from) unless from_clause.empty?
arel.lock(lock_value) if lock_value
arel
endfind_by_sql所使用的bound_attributes
def bound_attributes
if limit_value && !string_containing_comma?(limit_value)
limit_bind = Attribute.with_cast_value(
"LIMIT".freeze,
connection.sanitize_limit(limit_value),
Type::Value.new,
)
end
if offset_value
offset_bind = Attribute.with_cast_value(
"OFFSET".freeze,
offset_value.to_i,
Type::Value.new,
)
end
connection.combine_bind_parameters(
from_clause: from_clause.binds,
join_clause: arel.bind_values,
where_clause: where_clause.binds,
having_clause: having_clause.binds,
limit: limit_bind,
offset: offset_bind,
)
end检查find_by_sql接受了什么arel和bound_attributes
class ArticlesController < ApplicationController
def index
@articles = Article.where('title <> ?', 1).order(title: :asc)
byebug
@articles.each(&:object_id)
@articles
end发现sql已填充了值,binds中啥都没有
[1, 10] in /home/z/test_rails/dapo/app/controllers/articles_controller.rb
1: class ArticlesController < ApplicationController
2: def index
3: @articles = Article.where('title <> ?', 1).order(title: :asc)
4: byebug
=> 5: @articles.each(&:object_id)
6:
(byebug) break Article#find_by_sql
Successfully created breakpoint with id 1
(byebug) continue
Stopped by breakpoint 1 at /home/z/.rbenv/versions/2.3.3/lib/ruby/gems/2.3.0/gems/activerecord-5.0.2/lib/active_record/querying.rb:38
[33, 42] in /home/z/.rbenv/versions/2.3.3/lib/ruby/gems/2.3.0/gems/activerecord-5.0.2/lib/active_record/querying.rb
33: #
34: # You can use the same string replacement techniques as you can with ActiveRecord::QueryMethods#where:
35: #
36: # Post.find_by_sql ["SELECT title FROM posts WHERE author = ? AND created > ?", author_id, start_date]
37: # Post.find_by_sql ["SELECT body FROM comments WHERE author = :user_id OR approved_by = :user_id", { :user_id => user_id }]
=> 38: def find_by_sql(sql, binds = [], preparable: nil, &block)
39: result_set = connection.select_all(sanitize_sql(sql), "#{name} Load", binds, preparable: preparable)
40: column_types = result_set.column_types.dup
41: columns_hash.each_key { |k| column_types.delete k }
42: message_bus = ActiveSupport::Notifications.instrumenter
(byebug) sql.to_sql
"SELECT \"articles\".* FROM \"articles\" WHERE (title <> 1) ORDER BY \"articles\".\"title\" ASC"
(byebug) binds
[]
(byebug)不过select_all中似乎是可区分prepared_statement的,这个待研究(还有arel和bound_attributes)
def select_all(arel, name = nil, binds = [], preparable: nil)
arel, binds = binds_from_relation arel, binds
sql = to_sql(arel, binds)
if !prepared_statements || (arel.is_a?(String) && preparable.nil?)
preparable = false
else
preparable = visitor.preparable
end
if prepared_statements && preparable
select_prepared(sql, name, binds)
else
select(sql, name, binds)
end
endfind_by_sql最终返回的Array是由map那里生成的,instantiate会将查得的值塞到本类的实例中
def find_by_sql(sql, binds = [], preparable: nil, &block)
result_set = connection.select_all(sanitize_sql(sql), "#{name} Load", binds, preparable: preparable)
column_types = result_set.column_types.dup
columns_hash.each_key { |k| column_types.delete k }
message_bus = ActiveSupport::Notifications.instrumenter
payload = {
record_count: result_set.length,
class_name: name
}
message_bus.instrument("instantiation.active_record", payload) do
result_set.map { |record| instantiate(record, column_types, &block) }
end
end
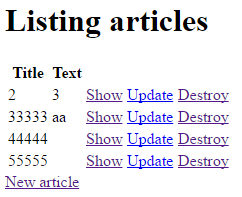
如上,是result_set含4个article的情况
where如何mixin到model上
ActiveRecord::Querying的实例方法where能在Article上调用,如无意外是extend了,检查一下
(byebug) Article.ancestors.select{|c| c.singleton_methods.include? :where}
[Article(id: integer, title: string, text: text, created_at: datetime, updated_at: datetime), ApplicationRecord(abstract), ActiveRecord::Base]确实是
$ lib git:(master) grep Querying -rn *
active_record/attributes.rb:150: # ==== \Querying
active_record/base.rb:282: extend Querying
active_record/querying.rb:2: module Querying
active_record.rb:55: autoload :Queryingeach如何mixin到Relation
module ActiveRecord
class Relation
include Enumerable
include FinderMethods, Calculations, SpawnMethods, QueryMethods, Batches, Explain, Delegation而Delegation
module ActiveRecord
module Delegation
delegate :to_xml, :encode_with, :length, :collect, :map, :each, :all?, :include?, :to_ary, :join,
:[], :&, :|, :+, :-, :sample, :reverse, :compact, :in_groups, :in_groups_of,
:to_sentence, :to_formatted_s,
:shuffle, :split, :index, to: :records